Introduction
In a significant move, banks have ramped up their lending activities to avoid a hefty 15% incremental tax slated to be imposed at the end of 2024. This strategic shift has led to a notable increase in the Advance-to-Deposit Ratio (ADR), which surged from 39% to 44% within a month. This article delves into the measures taken by banks, the implications of these actions, and how they align with the government’s fiscal policies.
Background
Taxation Pressure on Banks
In the fiscal year 2024-2025 budget, the government introduced a tax policy targeting banks with an ADR below 50%. This move aimed to leverage the significant profits banks recorded in 2023, which were nearly double compared to the previous year. Consequently, banks had to pivot their strategies to mitigate the potential tax burden.
Record-Breaking Lending Surge
In October 2024, banks’ lending activities skyrocketed by Rs1.1 trillion, marking a historic increase. Traditionally, banks preferred the safety of government securities for their investments. However, to meet the new tax requirements, they have now shifted focus towards increasing their loan portfolios.
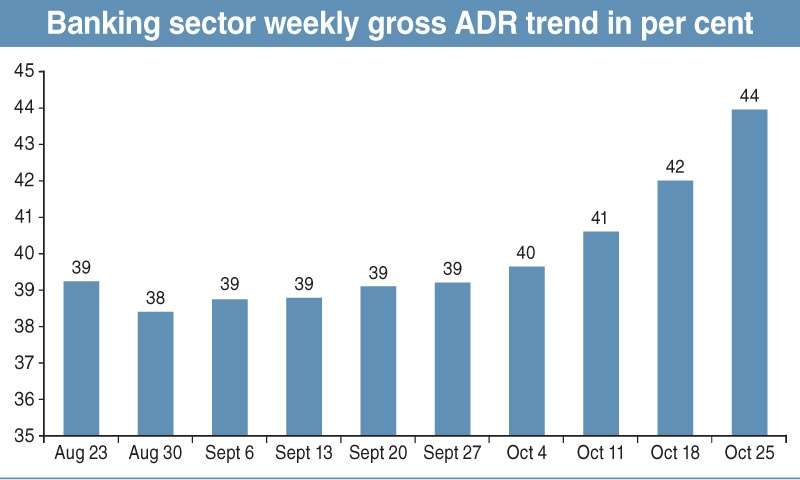
Increase in Advance-to-Deposit Ratio (ADR)
Significant ADR Jump
According to Mohammad Sohail, CEO of Topline Securities, the banking sector’s gross ADR ratio increased to 44% by October 25, 2024, up from 39% on September 27, 2024. This increase reflects the banks’ efforts to lend more and avoid the additional tax on lower ADRs.
Definition and Importance of ADR
The ADR is a crucial metric that indicates the proportion of total deposits that a bank lends out as advances. A higher ADR suggests a more aggressive lending strategy, which the government encouraged through the new tax policy.
Impact on Deposits
Decline in Deposits
To manage excess liquidity and reduce tax exposure, banks have taken measures to discourage large deposits. This approach has led to a decline in total deposits, which fell from Rs31.14 trillion on September 30 to Rs30.4 trillion by October 25.
Measures to Discourage Deposits
Banks have started charging fees on substantial deposits, especially those exceeding Rs5 billion. This unconventional step has been criticized for being against typical banking norms but is seen as necessary to meet the new fiscal requirements.
Lending Strategies
Focus on Short-Term Loans
Banks are reportedly directing a significant portion of their lending towards Development Finance Institutions (DFIs) for short-term loans. This strategy allows banks to boost their ADR temporarily and reduce their tax liability, as these funds are expected to return after the December 31 tax deadline.
Government Borrowing and Its Influence
The State Bank of Pakistan’s transfer of Rs2.7 trillion in profits to the government reduced the latter’s borrowing needs. Consequently, banks had to find alternative avenues for their funds, further driving the increase in lending.
Changes in Investment-to-Deposit Ratio (IDR)
Historical IDR Trends
The Investment-to-Deposit Ratio (IDR) saw a dramatic shift from 33% in 2007 to 88% in 2023, reaching 94% by June 2024. This trend indicates a long-term preference for investments in government securities.
Recent IDR Shifts
During the July-October 2024 period, banks were less able to invest heavily in government securities due to their focus on reducing deposits and increasing loans. This shift underscores the impact of the new tax policy on banking operations.
Implications and Future Outlook
Positive Outcomes
The surge in lending has several positive implications, including increased financial activity and potentially more economic growth. Banks’ adaptation to the new tax environment shows their resilience and ability to pivot strategies effectively.
Challenges and Criticisms
However, the measures to discourage deposits and the reliance on short-term lending raise concerns. Critics argue that these actions may undermine customer trust and could lead to instability in the financial sector.
Long-Term Strategies
Moving forward, banks will need to balance their lending activities with sustainable deposit management. The government’s fiscal policies will continue to play a significant role in shaping banking strategies.
Conclusion
Banks in Pakistan have demonstrated a strategic shift in response to new tax policies, significantly boosting their lending activities to avoid a 15% incremental tax. While this has led to a temporary decline in deposits and a shift away from government securities, it reflects the dynamic nature of the banking sector and its ability to adapt to regulatory changes. The long-term implications of these strategies will depend on how well banks can balance lending growth with deposit stability.
FAQs
1. What is the Advance-to-Deposit Ratio (ADR)?
The ADR is a measure of the proportion of a bank’s total deposits that are given out as loans. It indicates how much of the deposited money is being used for lending activities.
2. Why did banks increase their lending activities recently?
Banks increased their lending to avoid a 15% incremental tax imposed on those with an ADR below 50%, as stipulated in the fiscal year 2024-2025 budget.
3. How have banks discouraged large deposits?
To manage excess liquidity and reduce tax exposure, some banks have started charging fees on substantial deposits, particularly those exceeding Rs5 billion.
4. What is the Investment-to-Deposit Ratio (IDR)?
The IDR measures the proportion of a bank’s total deposits that are invested in government securities. It has historically been high, reflecting a preference for risk-free investments.
5. What are the implications of the recent lending surge for the banking sector?
The lending surge has increased financial activity and economic growth but has also led to a temporary decline in deposits and raised concerns about customer trust and financial stability.
ALSO READ:
https://flarenews.pk/2024/11/21/aaqib-javed-downplays-dual-role-as-national-selector-and-coach/